AI 概念
本节描述了 Spring AI 使用的核心概念。我们建议仔细阅读,以理解 Spring AI 实现背后的思想。
模型
AI 模型是旨在处理和生成信息的算法,通常模仿人类认知功能。通过从大型数据集中学习模式和洞察,这些模型可以进行预测、生成文本、图像或其他输出,从而增强各行业的各种应用。
AI 模型有许多不同的类型,每种都适用于特定的用例。虽然 ChatGPT 及其生成式 AI 功能通过文本输入和输出吸引了用户,但许多模型和公司提供了多样化的输入和输出。在 ChatGPT 之前,许多人对 Midjourney 和 Stable Diffusion 等文本到图像生成模型着迷。
下表根据模型的输入和输出类型对其进行了分类:
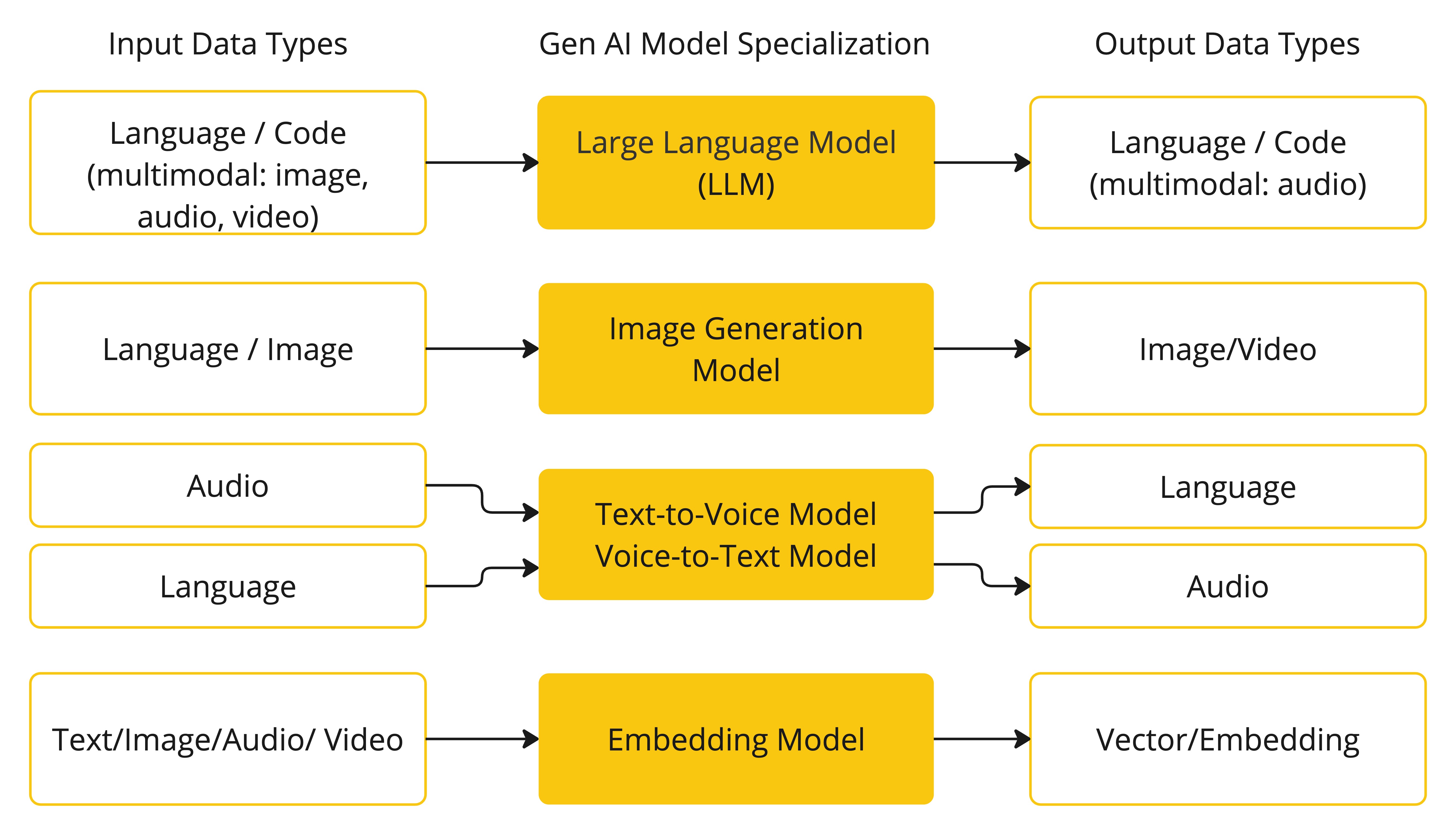
Spring AI 目前支持处理语言、图像和音频输入输出的模型。上表中的最后一行,接受文本作为输入并输出数字,更常被称为嵌入文本,代表了 AI 模型中使用的内部数据结构。Spring AI 支持嵌入,以实现更高级的用例。
像 GPT 这样的模型之所以与众不同,是因为它们的预训练性质,这在 GPT 中的“P”——Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer 中有所体现。这种预训练特性将 AI 转化为一种通用的开发工具,不需要广泛的机器学习或模型训练背景。
提示
提示是基于语言的输入的基础,它引导 AI 模型产生特定的输出。对于熟悉 ChatGPT 的人来说,提示可能看起来只是输入到对话框中并发送到 API 的文本。然而,它包含的内容远不止于此。在许多 AI 模型中,提示的文本不仅仅是一个简单的字符串。
ChatGPT 的 API 在一个提示中有多个文本输入,每个文本输入都被分配了一个角色。例如,有系统角色,它告诉模型如何行为并设置交互的上下文。还有用户角色,这通常是来自用户的输入。
制作有效的提示既是一门艺术,也是一门科学。ChatGPT 是为人类对话设计的。这与使用 SQL 等工具“提问”有很大的不同。必须像与另一个人交谈一样与 AI 模型进行交流。
这种交互风格的重要性使得“提示工程”成为一个独立的学科。有大量新兴技术可以提高提示的有效性。投入时间制作提示可以极大地改善结果输出。
分享提示已成为一种普遍的做法,并且正在对这个主题进行积极的学术研究。作为一个反直觉的例子,说明如何创建有效的提示(例如,与 SQL 对比),一篇 最近的研究论文 发现,你可以使用的最有效的提示之一以“深呼吸,然后一步一步地解决这个问题。”开头。这应该能让你明白语言为何如此重要。我们尚未完全理解如何最有效地利用这项技术以前的迭代,例如 ChatGPT 3.5,更不用说正在开发的新版本了。
提示模板
创建有效的提示涉及建立请求的上下文,并用特定于用户输入的值替换请求中的某些部分。
此过程使用传统的基于文本的模板引擎进行提示创建和管理。Spring AI 为此目的使用了 OSS 库 StringTemplate。
例如,考虑这个简单的提示模板:
Tell me a {adjective} joke about {content}.在 Spring AI 中,提示模板可以比作 Spring MVC 架构中的“视图”(View)。一个模型对象,通常是一个 java.util.Map,被提供来填充模板中的占位符。“渲染”后的字符串成为提供给 AI 模型的提示内容。
发送到模型的提示的具体数据格式存在很大的可变性。最初只是简单的字符串,提示已经演变为包含多条消息,其中每条消息中的每个字符串都代表模型的不同角色。
嵌入
嵌入是文本、图像或视频的数值表示,它们捕获输入之间的关系。
嵌入通过将文本、图像和视频转换为浮点数数组(称为向量)来工作。这些向量旨在捕获文本、图像和视频的含义。嵌入数组的长度称为向量的维度。
通过计算两个文本片段的向量表示之间的数值距离,应用程序可以确定用于生成嵌入向量的对象之间的相似性。
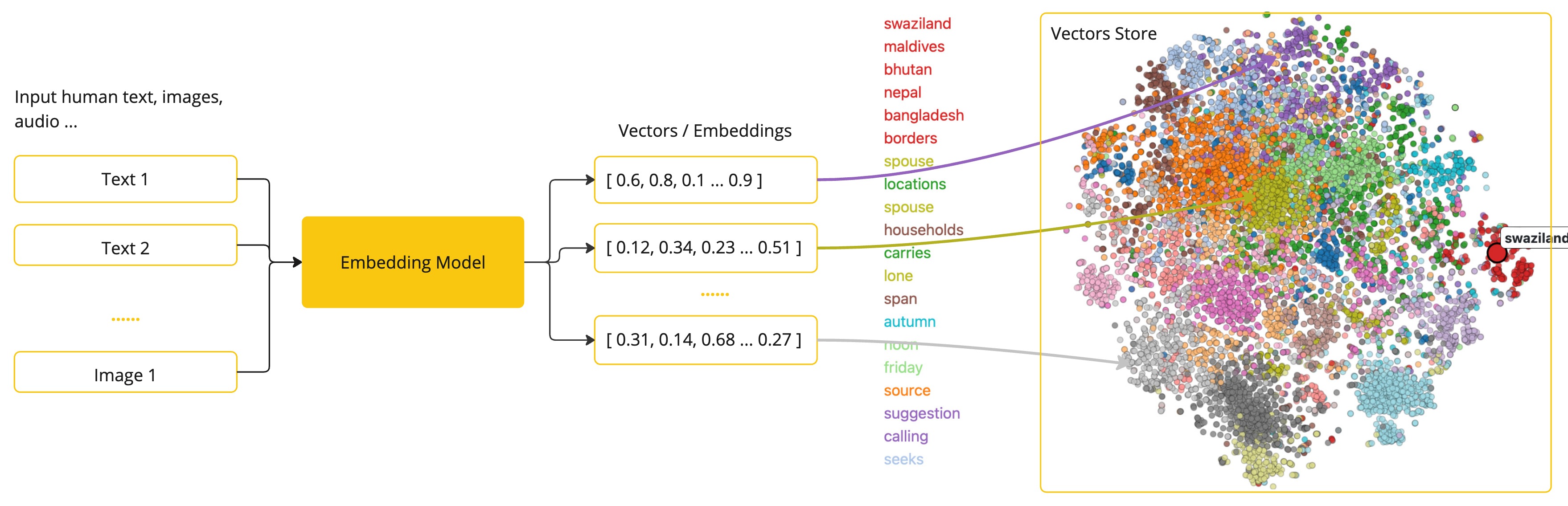
作为一名探索 AI 的 Java 开发人员,无需理解这些向量表示背后复杂的数学理论或具体的实现。只需对它们在 AI 系统中的作用和功能有一个基本的了解就足够了,尤其是在将 AI 功能集成到应用程序中时。
嵌入在像检索增强生成 (RAG) 模式这样的实际应用中特别相关。它们能够将数据表示为语义空间中的点,这类似于欧几里得几何的二维空间,但维度更高。这意味着,就像欧几里得几何中平面上的点可以根据它们的坐标而靠近或远离一样,在语义空间中,点的接近度反映了意义上的相似性。关于相似主题的句子在这个多维空间中位置更近,就像图表上彼此靠近的点一样。这种接近性有助于文本分类、语义搜索,甚至产品推荐等任务,因为它允许 AI 根据这些扩展语义景观中的“位置”来识别和分组相关概念。
您可以将此语义空间视为一个向量。
令牌
令牌是 AI 模型工作方式的构建块。在输入时,模型将单词转换为令牌。在输出时,它们将令牌转换回单词。
在英语中,一个令牌大约对应一个单词的 75%。作为参考,莎士比亚的全部作品,总计约 90 万字,大约转换为 120 万个令牌。

也许更重要的是,令牌 = 金钱。在托管 AI 模型的上下文中,您的费用由使用的令牌数量决定。输入和输出都计入总令牌数。
此外,模型受令牌限制,这限制了单个 API 调用中处理的文本量。此阈值通常称为“上下文窗口”。模型不会处理任何超出此限制的文本。
例如,ChatGPT3 有 4K 令牌限制,而 GPT4 提供不同的选项,例如 8K、16K 和 32K。Anthropic 的 Claude AI 模型具有 100K 令牌限制,Meta 最近的研究产生了一个 1M 令牌限制模型。
要用 GPT4 总结莎士比亚的全部作品,您需要设计软件工程策略来切分数据并将数据呈现在模型的上下文窗口限制内。Spring AI 项目可以帮助您完成这项任务。
结构化输出
AI 模型的输出传统上是以 java.lang.String 的形式出现的,即使您要求回复是 JSON 格式。它可能是一个正确的 JSON,但它不是 JSON 数据结构。它只是一个字符串。此外,在提示中要求“JSON 格式”并不是 100% 准确。
这种复杂性导致了一个专门领域的出现,涉及创建提示以产生预期的输出,然后将生成的简单字符串转换为可用于应用程序集成的可用数据结构。
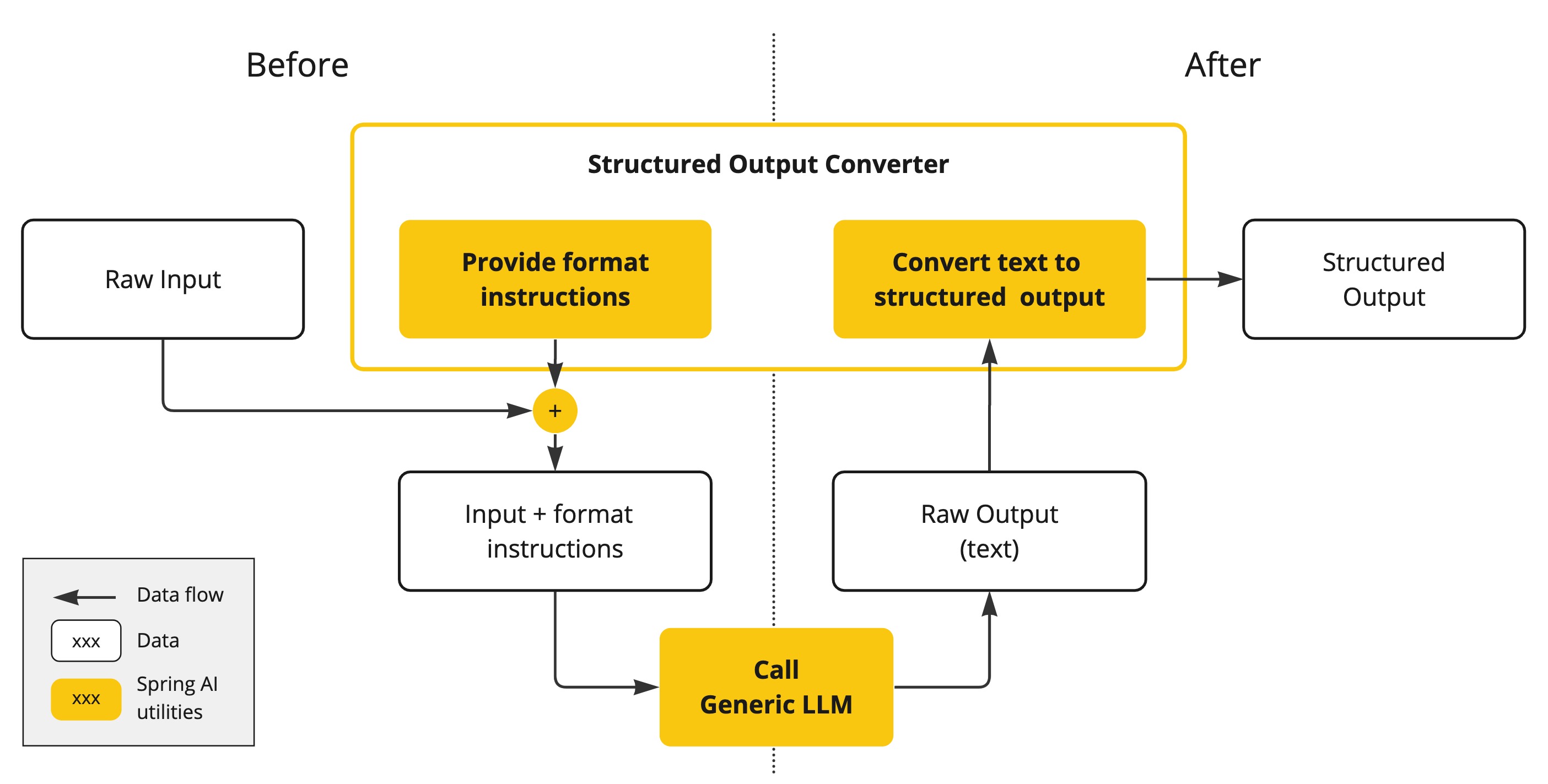
结构化输出转换 采用精心设计的提示,通常需要与模型进行多次交互才能实现所需的格式。
将您的数据和 API 带到 AI 模型
您如何为 AI 模型提供它尚未训练过的信息?
请注意,GPT 3.5/4.0 数据集仅截至 2021 年 9 月。因此,模型表示它不知道需要该日期之后知识的问题的答案。一个有趣的趣闻是,这个数据集大约有 650GB。
有三种技术可以定制 AI 模型以整合您的数据:
-
微调(Fine Tuning):这种传统的机器学习技术涉及调整模型并更改其内部权重。然而,对于机器学习专家来说,这是一个具有挑战性的过程,并且由于像 GPT 这样模型的规模,它对资源的需求极大。此外,有些模型可能不提供此选项。
-
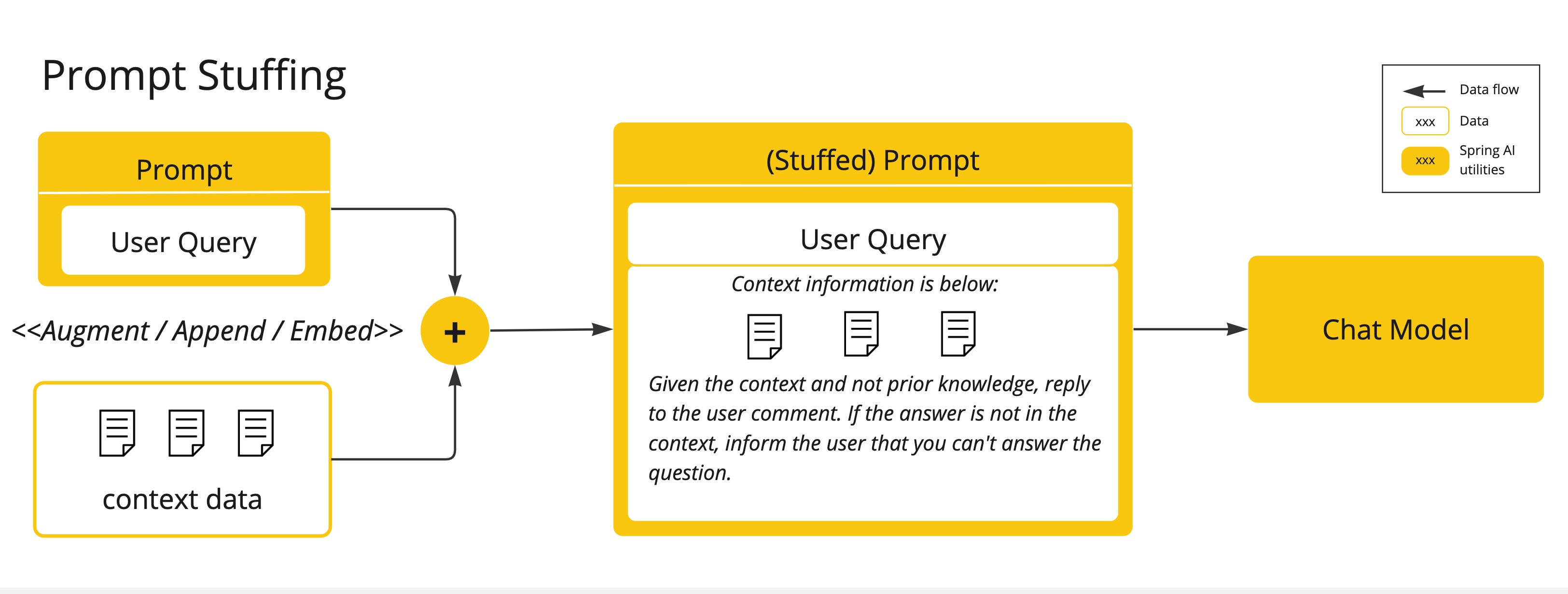
提示填充(Prompt Stuffing):一个更实用的替代方法是将您的数据嵌入到提供给模型的提示中。鉴于模型的令牌限制,需要一些技术来在模型的上下文窗口中呈现相关数据。这种方法通俗地称为“
填充提示”。Spring AI 库可以帮助您实现基于“填充提示”技术(也称为 检索增强生成 (RAG))的解决方案。
-
工具调用(Tool Calling):此技术允许注册工具(用户定义的 servicio),这些工具将大型语言模型连接到外部系统的 API。Spring AI 极大地简化了您为支持 工具调用 而需要编写的代码。
检索增强生成
一种称为检索增强生成 (RAG) 的技术已经出现,旨在解决将相关数据整合到提示中以实现准确的 AI 模型响应的挑战。
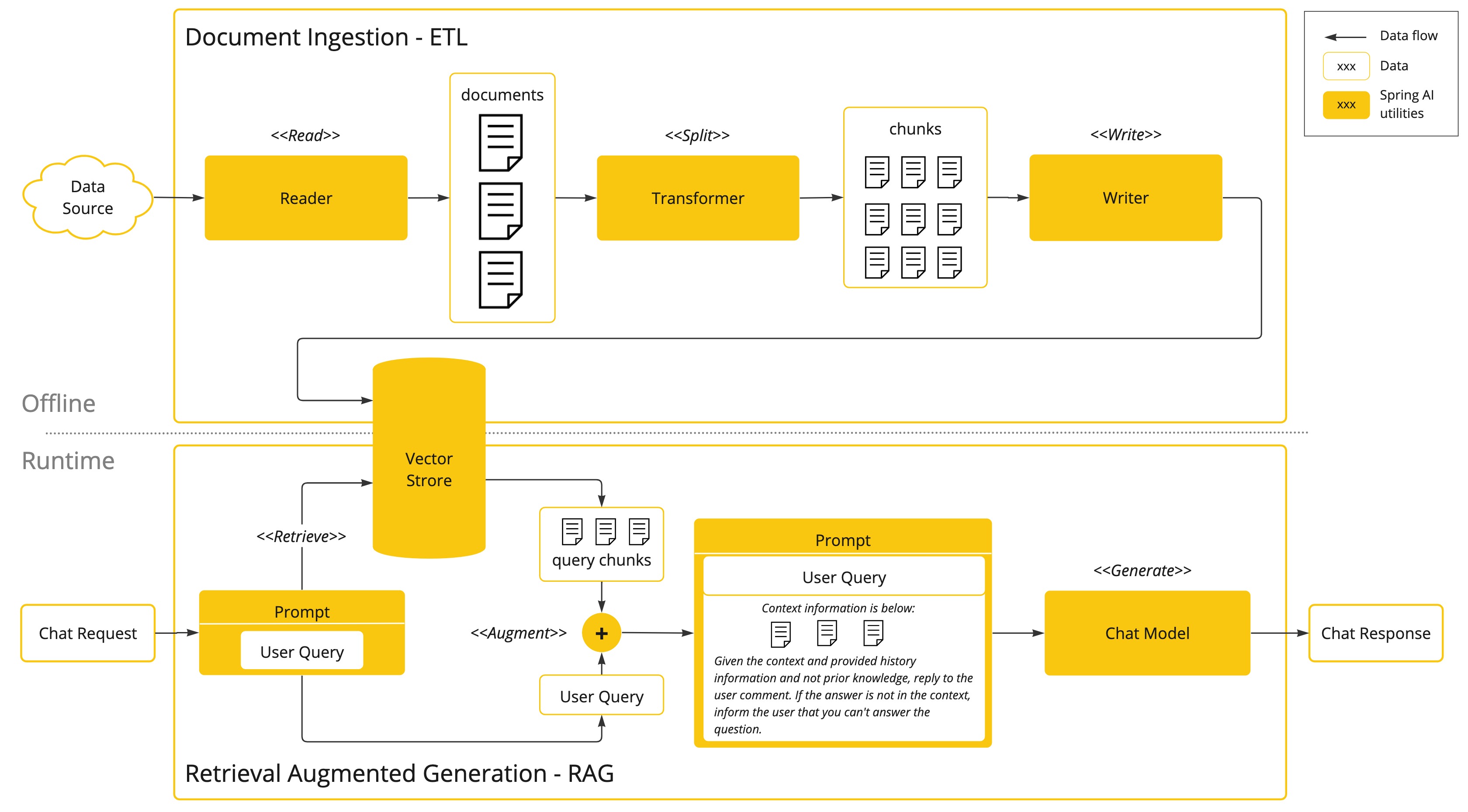
该方法涉及批处理风格的编程模型,其中作业从您的文档中读取非结构化数据,对其进行转换,然后将其写入向量数据库。从高层次来看,这是一个 ETL(提取、转换和加载)管道。向量数据库用于 RAG 技术中的检索部分。
作为将非结构化数据加载到向量数据库的一部分,最重要的转换之一是将原始文档分割成更小的片段。将原始文档分割成更小片段的过程有两个重要步骤:
-
在保留内容语义边界的同时将文档分割成多个部分。例如,对于包含段落和表格的文档,应避免在段落或表格中间分割文档。对于代码,应避免在方法实现中间分割代码。
-
将文档的各个部分进一步分割成大小仅占 AI 模型令牌限制一小部分的片段。
RAG 的下一个阶段是处理用户输入。当用户的问题要由 AI 模型回答时,问题和所有“相似”的文档片段都放在发送给 AI 模型的提示中。这就是使用向量数据库的原因。它非常擅长查找相似内容。
-
ETL 管道 提供了关于编排从数据源提取数据并将其存储到结构化向量存储的流程的进一步信息,确保数据以最佳格式存储,以便在将其传递给 AI 模型时进行检索。
-
ChatClient - RAG 解释了如何使用
QuestionAnswerAdvisor在您的应用程序中启用 RAG 功能。
工具调用
大型语言模型 (LLM) 在训练后是冻结的,导致知识陈旧,并且无法访问或修改外部数据。
工具调用 机制解决了这些缺点。它允许您将自己的服务注册为工具,以将大型语言模型连接到外部系统的 API。这些系统可以为 LLM 提供实时数据并代表它们执行数据处理操作。
Spring AI 极大地简化了您为支持工具调用而需要编写的代码。它为您处理工具调用对话。您可以将您的工具作为 @Tool 注释的方法提供,并将其包含在您的提示选项中,以使其可供模型使用。此外,您可以在单个提示中定义和引用多个工具。
-
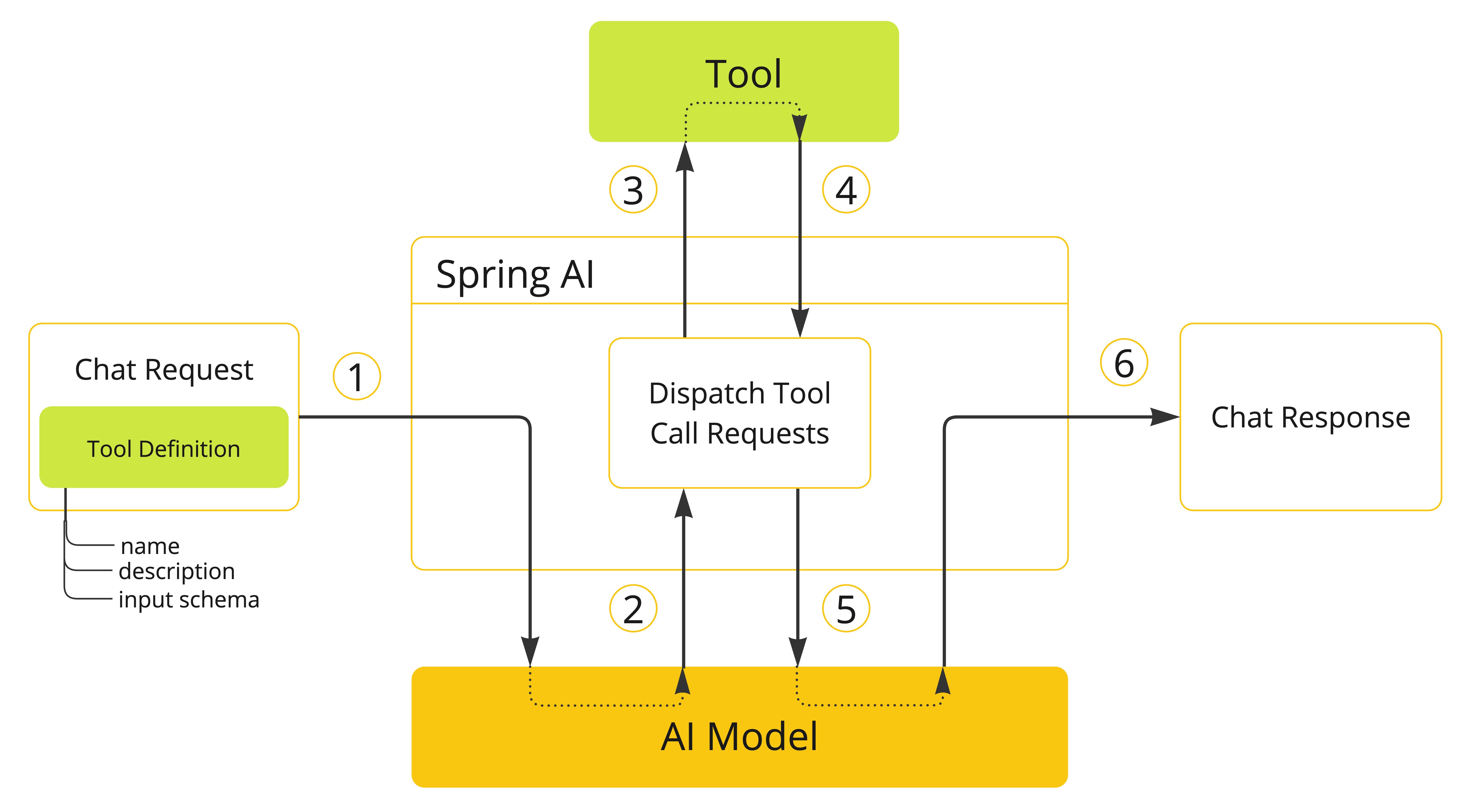
当我们要使工具可供模型使用时,我们将其定义包含在聊天请求中。每个工具定义都包含名称、描述和输入参数的模式。
-
当模型决定调用工具时,它会发送一个包含工具名称和根据定义模式建模的输入参数的响应。
-
应用程序负责使用工具名称识别并执行工具,并提供输入参数。
-
工具调用的结果由应用程序处理。
-
应用程序将工具调用结果发送回模型。
-
模型使用工具调用结果作为附加上下文生成最终响应。
有关如何将此功能与不同 AI 模型一起使用的更多信息,请参阅 工具调用 文档。
评估 AI 响应
有效评估 AI 系统对用户请求的输出对于确保最终应用程序的准确性和实用性非常重要。几种新兴技术允许为此目的使用预训练模型本身。
此评估过程涉及分析生成的响应是否与用户意图和查询上下文一致。相关性、连贯性和事实正确性等指标用于衡量 AI 生成响应的质量。
一种方法是将用户的请求和 AI 模型的响应都呈现给模型,查询响应是否与提供的数据一致。
此外,利用存储在向量数据库中的信息作为补充数据可以增强评估过程,有助于确定响应的相关性。
Spring AI 项目提供了一个 Evaluator API,目前可以访问评估模型响应的基本策略。有关更多信息,请参阅 评估测试 文档。