构建高效智能体
在最近的研究出版物 构建高效智能体 中,Anthropic 分享了关于构建高效大型语言模型(LLM)智能体的宝贵见解。这项研究的特别之处在于,它强调了简单性和可组合性优于复杂的框架。让我们探讨这些原则如何通过 Spring AI 转化为实际实现。 image::https://raw.githubusercontent.com/spring-io/spring-io-static/refs/heads/main/blog/tzolov/spring-ai-agentic-systems.jpg[] 虽然模式描述和图表来源于 Anthropic 的原始出版物,但我们将重点介绍如何使用 Spring AI 的模型可移植性和结构化输出功能来实现这些模式。我们建议您首先阅读原始论文。 spring-ai-examples 仓库中的 agentic-patterns 目录包含以下所有示例的代码。
智能体系统
研究出版物对两种类型的智能体系统进行了重要的架构区分:
-
工作流:通过预定义代码路径(例如,规范系统)编排 LLM 和工具的系统
-
智能体:LLM 动态指导其自身流程和工具使用的系统
关键的见解是,虽然完全自主的智能体可能看起来很有吸引力,但工作流通常为明确定义的任务提供更好的可预测性和一致性。这与企业对可靠性和可维护性的关键要求完全吻合。
让我们研究 Spring AI 如何通过五种基本模式实现这些概念,每种模式都服务于特定的用例:
1. 链式工作流
链式工作流模式体现了将复杂任务分解为更简单、更易于管理的步骤的原则。
何时使用: - 具有清晰顺序步骤的任务 - 当您希望牺牲延迟以获得更高准确性时 - 当每个步骤都基于上一步的输出时
以下是 Spring AI 实现中的一个实际示例:
public class ChainWorkflow {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
private final String[] systemPrompts;
public String chain(String userInput) {
String response = userInput;
for (String prompt : systemPrompts) {
String input = String.format("{%s}\n {%s}", prompt, response);
response = chatClient.prompt(input).call().content();
}
return response;
}
}此实现演示了几个关键原则:
-
每个步骤都有一个集中的职责
-
一个步骤的输出成为下一个步骤的输入
-
链易于扩展和维护
2. 并行化工作流
LLM 可以同时处理任务,并通过编程方式聚合其输出。
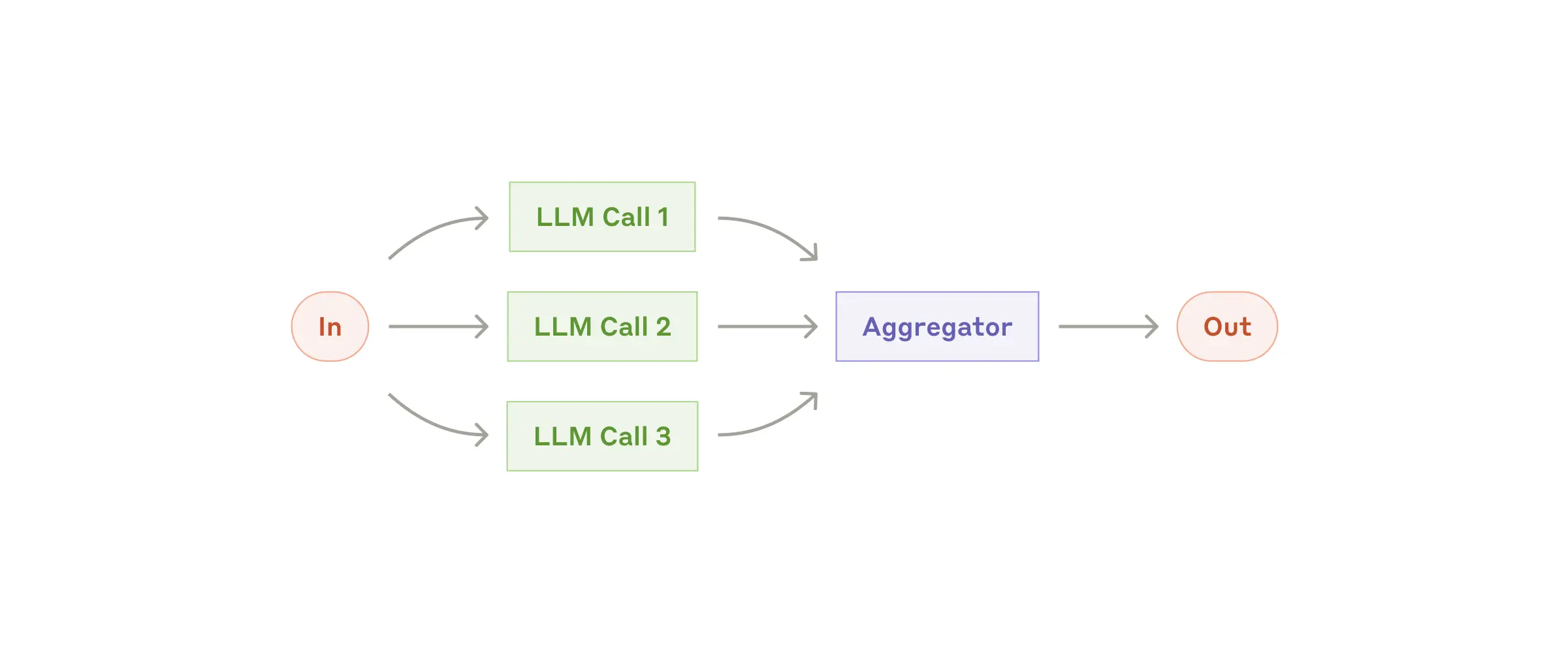
何时使用: - 处理大量相似但独立的项目 - 需要多个独立视角的任务 - 当处理时间至关重要且任务可并行化时
List<String> parallelResponse = new ParallelizationWorkflow(chatClient)
.parallel(
"Analyze how market changes will impact this stakeholder group.",
List.of(
"Customers: ...",
"Employees: ...",
"Investors: ...",
"Suppliers: ..."
),
4
);3. 路由工作流
路由模式实现智能任务分发,为不同类型的输入提供专门处理。
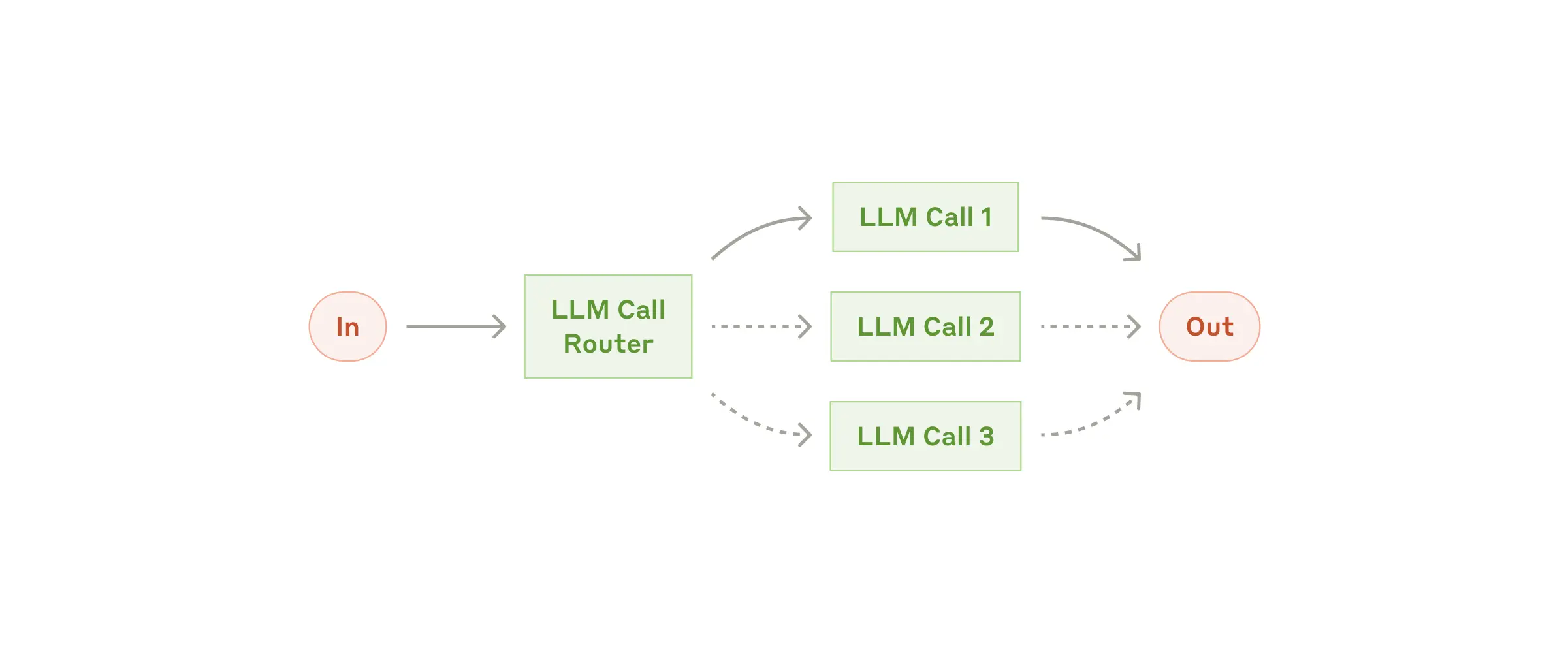
何时使用: - 具有不同输入类别的复杂任务 - 当不同输入需要专门处理时 - 当分类可以准确处理时
@Autowired
private ChatClient chatClient;
RoutingWorkflow workflow = new RoutingWorkflow(chatClient);
Map<String, String> routes = Map.of(
"billing", "You are a billing specialist. Help resolve billing issues...",
"technical", "You are a technical support engineer. Help solve technical problems...",
"general", "You are a customer service representative. Help with general inquiries..."
);
String input = "My account was charged twice last week";
String response = workflow.route(input, routes);4. 编排器-工作器
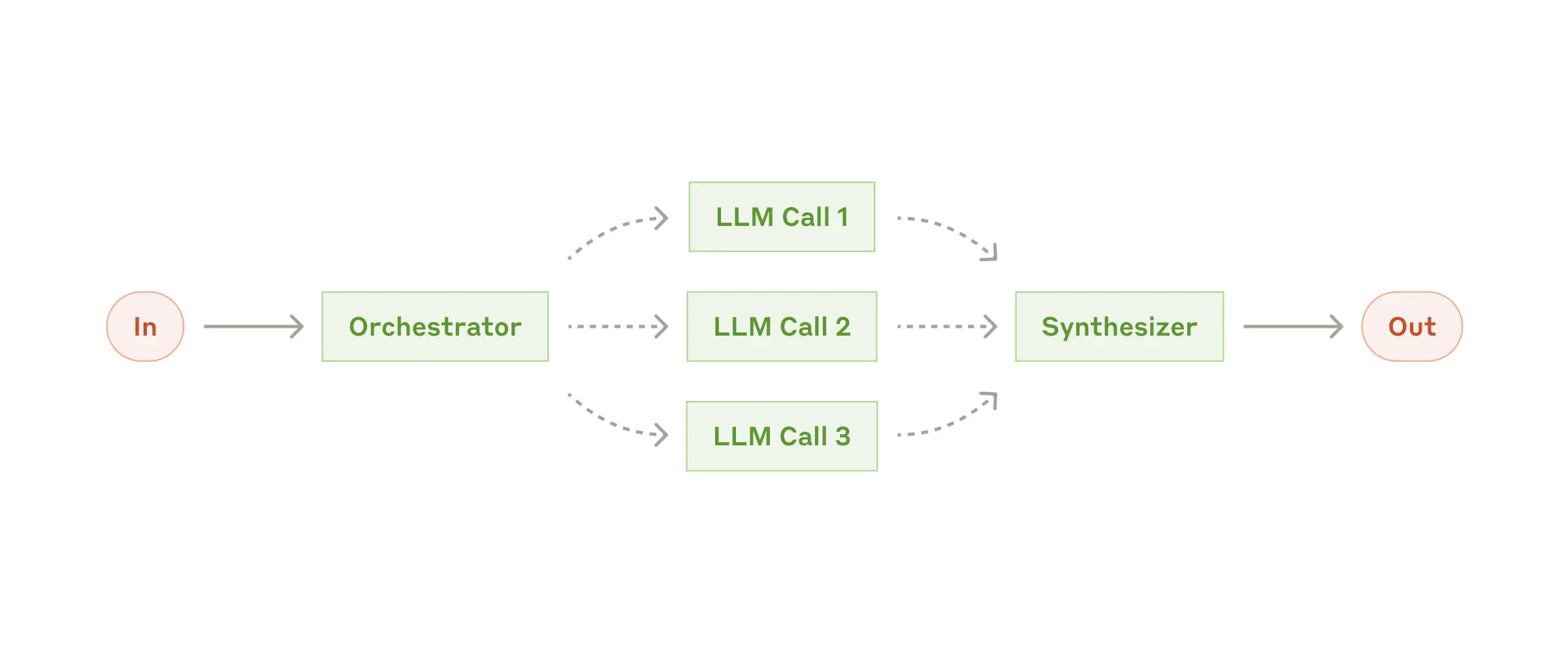
何时使用: - 无法预先预测子任务的复杂任务 - 需要不同方法或视角的任务 - 需要自适应问题解决的情况
public class OrchestratorWorkersWorkflow {
public WorkerResponse process(String taskDescription) {
// 1. Orchestrator analyzes task and determines subtasks
OrchestratorResponse orchestratorResponse = // ...
// 2. Workers process subtasks in parallel
List<String> workerResponses = // ...
// 3. Results are combined into final response
return new WorkerResponse(/*...*/);
}
}使用示例:
ChatClient chatClient = // ... initialize chat client
OrchestratorWorkersWorkflow workflow = new OrchestratorWorkersWorkflow(chatClient);
WorkerResponse response = workflow.process(
"Generate both technical and user-friendly documentation for a REST API endpoint"
);
System.out.println("Analysis: " + response.analysis());
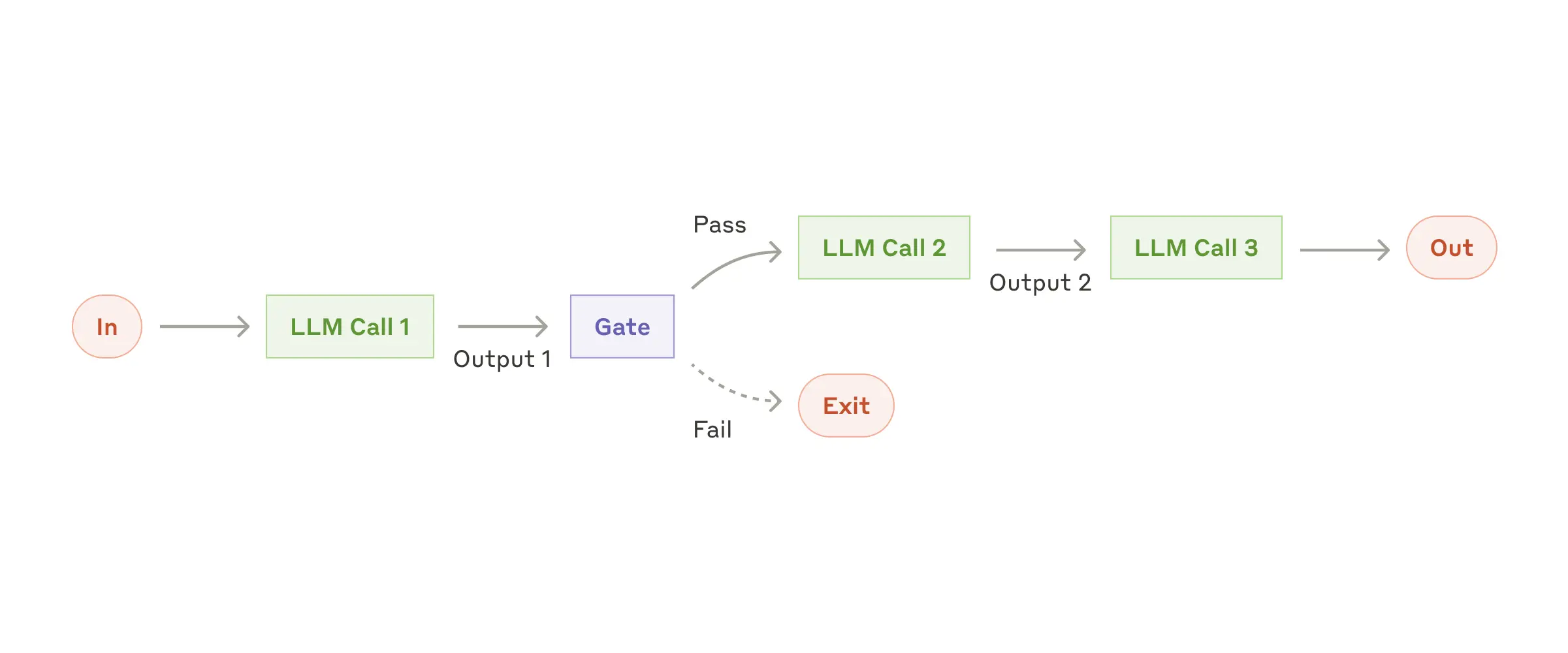
System.out.println("Worker Outputs: " + response.workerResponses());5. 评估器-优化器
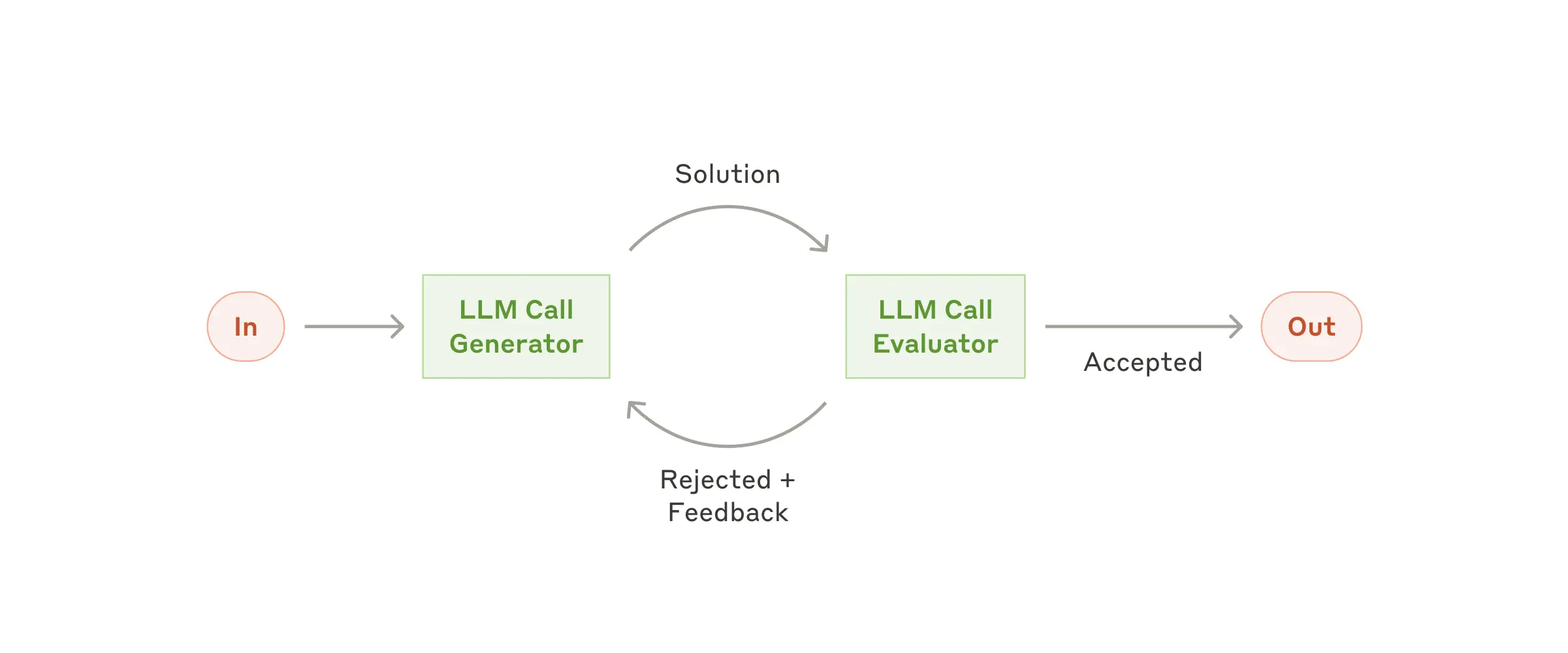
何时使用: - 存在明确的评估标准 - 迭代优化提供可衡量价值 - 任务受益于多轮批判
public class EvaluatorOptimizerWorkflow {
public RefinedResponse loop(String task) {
Generation generation = generate(task, context);
EvaluationResponse evaluation = evaluate(generation.response(), task);
return new RefinedResponse(finalSolution, chainOfThought);
}
}使用示例:
ChatClient chatClient = // ... initialize chat client
EvaluatorOptimizerWorkflow workflow = new EvaluatorOptimizerWorkflow(chatClient);
RefinedResponse response = workflow.loop(
"Create a Java class implementing a thread-safe counter"
);
System.out.println("Final Solution: " + response.solution());
System.out.println("Evolution: " + response.chainOfThought());Spring AI 的实现优势
Spring AI 对这些模式的实现提供了与 Anthropic 建议相符的几个优点:
模型可移植性
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-openai-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>结构化输出
EvaluationResponse response = chatClient.prompt(prompt)
.call()
.entity(EvaluationResponse.class);一致的 API
-
跨不同 LLM 提供商的统一接口
-
内置错误处理和重试
-
灵活的提示管理
最佳实践和建议
-
从简单开始
-
在增加复杂性之前,从基本工作流开始
-
使用满足您需求的最简单模式
-
仅在需要时增加复杂性
-
为可靠性设计
-
实现清晰的错误处理
-
尽可能使用类型安全响应
-
在每个步骤中构建验证
-
考虑权衡
-
平衡延迟与准确性
-
评估何时使用并行处理
-
在固定工作流和动态智能体之间进行选择