提示词
提示词是引导 AI 模型生成特定输出的输入。
这些提示词的设计和措辞显著影响模型的响应。
在 Spring AI 中与 AI 模型交互的最低层,处理提示词有点类似于在 Spring MVC 中管理“视图”。
这涉及创建带有动态内容占位符的 extenso 文本。
然后根据用户请求或应用程序中的其他代码替换这些占位符。
另一个类比是包含某些表达式占位符的 SQL 语句。
随着 Spring AI 的发展,它将引入更高级别的抽象来与 AI 模型交互。
本节中描述的基础类在作用和功能上可以类比为 JDBC。
例如,ChatModel 类类似于 JDK 中的核心 JDBC 库。
ChatClient 类可以类比为 JdbcClient,它构建在 ChatModel 之上,并通过 Advisor 提供更高级的构造,
以考虑与模型的过去交互,用额外的上下文文档增强提示词,并引入代理行为。
提示词的结构在 AI 领域中随着时间的推移而演变。
最初,提示词是简单的字符串。
随着时间的推移,它们包含了特定输入的占位符,例如 AI 模型识别的“USER:”。
OpenAI 通过将多个消息字符串分类为不同的角色,然后在 AI 模型处理它们之前,为提示词引入了更多的结构。
API 概述
提示词
通常使用 ChatModel 的 call() 方法,该方法接受一个 Prompt 实例并返回一个 ChatResponse。
Prompt 类充当组织化的 Message 对象序列和请求 ChatOptions 的容器。
每个 Message 在提示词中都扮演着独特的角色,其内容和意图各不相同。
这些角色可以包含各种元素,从用户查询到 AI 生成的响应,再到相关的背景信息。
这种安排使得与 AI 模型进行复杂而详细的交互成为可能,因为提示词是由多条消息构建而成的,每条消息在对话中都扮演着特定的角色。
下面是 Prompt 类的截断版本,为简洁起见,省略了构造函数和实用方法:
public class Prompt implements ModelRequest<List<Message>> {
private final List<Message> messages;
private ChatOptions chatOptions;
}消息
Message 接口封装了 Prompt 的文本内容、元数据属性集合以及称为 MessageType 的分类。
该接口定义如下:
public interface Content {
String getContent();
Map<String, Object> getMetadata();
}
public interface Message extends Content {
MessageType getMessageType();
}多模态消息类型还实现了 MediaContent 接口,提供了 Media 内容对象的列表。
public interface MediaContent extends Content {
Collection<Media> getMedia();
}Message 接口的各种实现对应于 AI 模型可以处理的不同类别的消息。
模型根据对话角色区分消息类别。
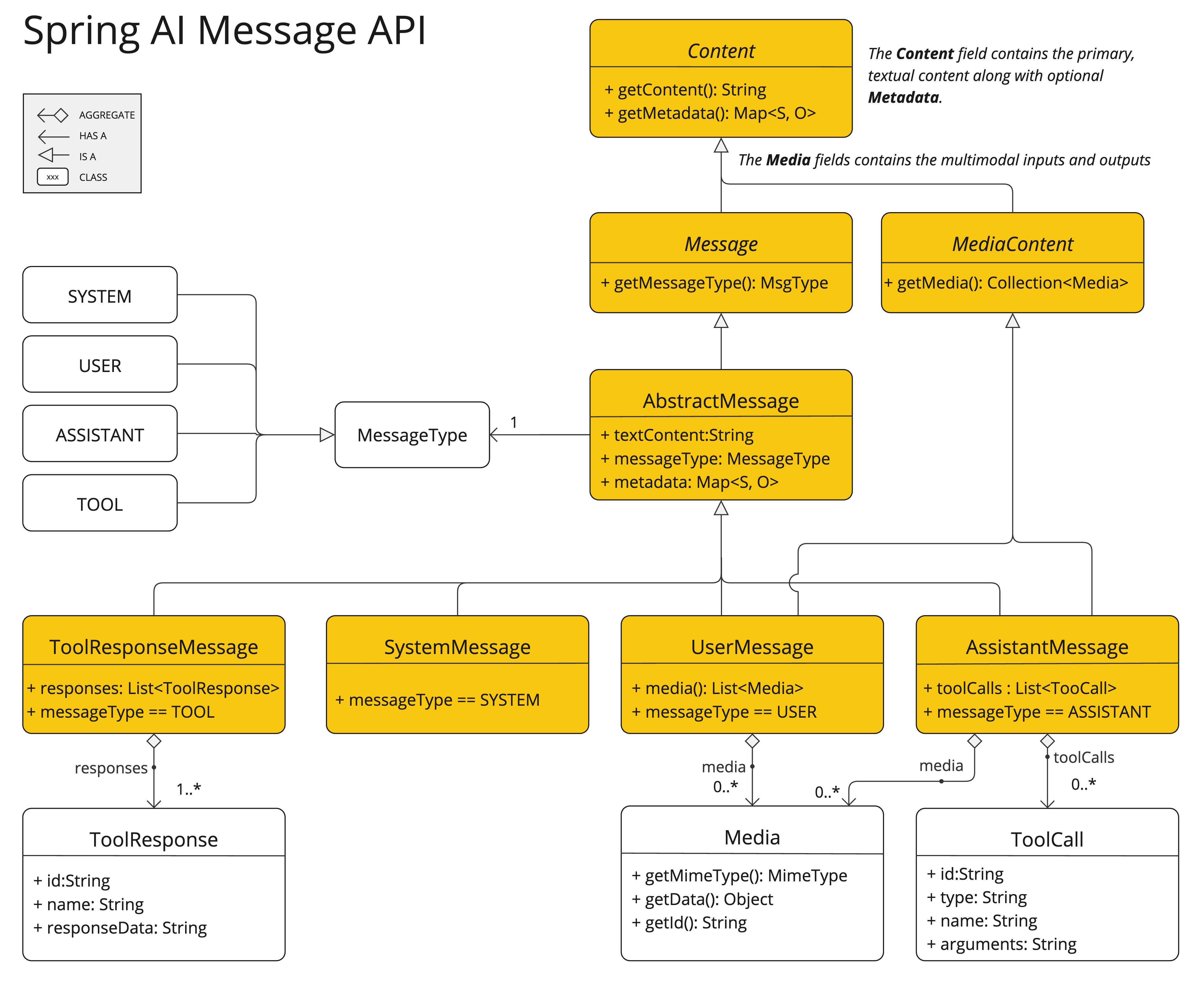
这些角色通过 MessageType 有效地映射,如下所述。
角色
每条消息都分配有一个特定的角色。 这些角色对消息进行分类,为 AI 模型阐明了提示词每个部分的上下文和目的。 这种结构化方法增强了与 AI 通信的细微差别和有效性,因为提示词的每个部分在交互中都扮演着独特而明确的角色。
主要角色是:
-
系统角色:引导 AI 的行为和响应风格,为 AI 如何解释和回复输入设置参数或规则。它类似于在开始对话之前向 AI 提供指令。
-
用户角色:代表用户的输入——他们向 AI 提出的问题、命令或陈述。这个角色是基础,因为它构成了 AI 响应的基础。
-
助手角色:AI 对用户输入的响应。 它不仅仅是一个答案或反应,对于维持对话流程至关重要。 通过跟踪 AI 之前的响应(其“助手角色”消息),系统确保了连贯且上下文相关的交互。 助手消息还可能包含函数工具调用请求信息。 它就像 AI 中的一个特殊功能,在需要执行特定功能时使用,例如计算、获取数据或除了交谈之外的其他任务。
-
工具/函数角色:工具/函数角色侧重于响应工具调用助手消息返回附加信息。
角色在 Spring AI 中表示为枚举,如下所示:
public enum MessageType {
USER("user"),
ASSISTANT("assistant"),
SYSTEM("system"),
TOOL("tool");
...
}提示模板
Spring AI 中用于提示词模板化的一个关键组件是 PromptTemplate 类,它旨在促进创建结构化提示词,然后将其发送到 AI 模型进行处理。
public class PromptTemplate implements PromptTemplateActions, PromptTemplateMessageActions {
// Other methods to be discussed later
}这个类使用 TemplateRenderer API 来渲染模板。默认情况下,Spring AI 使用 StTemplateRenderer 实现,它基于 Terence Parr 开发的开源 StringTemplate 引擎。模板变量由 {} 语法标识,但您也可以配置分隔符以使用其他语法。
public interface TemplateRenderer extends BiFunction<String, Map<String, Object>, String> {
@Override
String apply(String template, Map<String, Object> variables);
}Spring AI 使用 TemplateRenderer 接口来处理变量到模板字符串的实际替换。
默认实现使用 [StringTemplate]。
如果您需要自定义逻辑,可以提供自己的 TemplateRenderer 实现。
对于不需要模板渲染的场景(例如,模板字符串已经完成),您可以使用提供的 NoOpTemplateRenderer。
PromptTemplate promptTemplate = PromptTemplate.builder()
.renderer(StTemplateRenderer.builder().startDelimiterToken('<').endDelimiterToken('>').build())
.template("""
Tell me the names of 5 movies whose soundtrack was composed by <composer>.
""")
.build();
String prompt = promptTemplate.render(Map.of("composer", "John Williams"));该类实现的接口支持提示词创建的不同方面:
PromptTemplateStringActions 专注于创建和渲染提示词字符串,代表最基本的提示词生成形式。
PromptTemplateMessageActions 专为通过生成和操作 Message 对象来创建提示词而定制。
PromptTemplateActions 旨在返回 Prompt 对象,该对象可以传递给 ChatModel 以生成响应。
虽然这些接口在许多项目中可能不会被广泛使用,但它们展示了提示词创建的不同方法。
实现的接口是
public interface PromptTemplateStringActions {
String render();
String render(Map<String, Object> model);
}方法 String render():将提示词模板渲染成最终字符串格式,无需外部输入,适用于没有占位符或动态内容的模板。
方法 String render(Map<String, Object> model):增强渲染功能以包含动态内容。它使用 Map<String, Object>,其中 map 键是提示词模板中的占位符名称,值是要插入的动态内容。
public interface PromptTemplateMessageActions {
Message createMessage();
Message createMessage(List<Media> mediaList);
Message createMessage(Map<String, Object> model);
}方法 Message createMessage():创建不带附加数据的 Message 对象,用于静态或预定义的消息内容。
方法 Message createMessage(List<Media> mediaList):创建包含静态文本和媒体内容的 Message 对象。
方法 Message createMessage(Map<String, Object> model):扩展消息创建以集成动态内容,接受 Map<String, Object>,其中每个条目表示消息模板中的占位符及其对应的动态值。
public interface PromptTemplateActions extends PromptTemplateStringActions {
Prompt create();
Prompt create(ChatOptions modelOptions);
Prompt create(Map<String, Object> model);
Prompt create(Map<String, Object> model, ChatOptions modelOptions);
}方法 Prompt create():生成不带外部数据输入的 Prompt 对象,适用于静态或预定义提示词。
方法 Prompt create(ChatOptions modelOptions):生成不带外部数据输入且带有聊天请求特定选项的 Prompt 对象。
方法 Prompt create(Map<String, Object> model):扩展提示词创建功能以包含动态内容,接受 Map<String, Object>,其中每个 map 条目是提示词模板中的占位符及其关联的动态值。
方法 Prompt create(Map<String, Object> model, ChatOptions modelOptions):扩展提示词创建功能以包含动态内容,接受 Map<String, Object>,其中每个 map 条目是提示词模板中的占位符及其关联的动态值,以及聊天请求的特定选项。
使用示例
下面是一个简单的示例,取自 AI Workshop on PromptTemplates。
PromptTemplate promptTemplate = new PromptTemplate("Tell me a {adjective} joke about {topic}");
Prompt prompt = promptTemplate.create(Map.of("adjective", adjective, "topic", topic));
return chatModel.call(prompt).getResult();下面是另一个示例,取自 AI Workshop on Roles。
String userText = """
Tell me about three famous pirates from the Golden Age of Piracy and why they did.
Write at least a sentence for each pirate.
""";
Message userMessage = new UserMessage(userText);
String systemText = """
You are a helpful AI assistant that helps people find information.
Your name is {name}
You should reply to the user's request with your name and also in the style of a {voice}.
""";
SystemPromptTemplate systemPromptTemplate = new SystemPromptTemplate(systemText);
Message systemMessage = systemPromptTemplate.createMessage(Map.of("name", name, "voice", voice));
Prompt prompt = new Prompt(List.of(userMessage, systemMessage));
List<Generation> response = chatModel.call(prompt).getResults();这展示了如何通过使用 SystemPromptTemplate 创建带有系统角色的 Message 并传入占位符值来构建 Prompt 实例。
然后将具有 user 角色的消息与具有 system 角色的消息组合起来形成提示词。
然后将提示词传递给 ChatModel 以获得生成响应。
使用自定义模板渲染器
您可以通过实现 TemplateRenderer 接口并将其传递给 PromptTemplate 构造函数来使用自定义模板渲染器。您也可以继续使用默认的 StTemplateRenderer,但使用自定义配置。
默认情况下,模板变量由 {} 语法标识。如果您计划在提示词中包含 JSON,您可能希望使用不同的语法以避免与 JSON 语法冲突。例如,您可以使用 < 和 > 分隔符。
PromptTemplate promptTemplate = PromptTemplate.builder()
.renderer(StTemplateRenderer.builder().startDelimiterToken('<').endDelimiterToken('>').build())
.template("""
Tell me the names of 5 movies whose soundtrack was composed by <composer>.
""")
.build();
String prompt = promptTemplate.render(Map.of("composer", "John Williams"));使用资源而不是原始字符串
Spring AI 支持 org.springframework.core.io.Resource 抽象,因此您可以将提示词数据放在可以直接在 PromptTemplate 中使用的文件中。
例如,您可以在 Spring 管理的组件中定义一个字段来检索 Resource。
@Value("classpath:/prompts/system-message.st")
private Resource systemResource;然后直接将该资源传递给 SystemPromptTemplate。
SystemPromptTemplate systemPromptTemplate = new SystemPromptTemplate(systemResource);提示词工程
在生成式 AI 中,提示词的创建是开发者的一项关键任务。 这些提示词的质量和结构显著影响 AI 输出的有效性。 投入时间和精力设计周密的提示词可以大大提高 AI 的结果。
共享和讨论提示词是 AI 社区中的常见做法。 这种协作方法不仅创造了一个共享的学习环境,而且还促成了高效提示词的识别和使用。
该领域的研究通常涉及分析和比较不同的提示词,以评估它们在各种情况下的有效性。 例如,一项重要研究表明,以“深呼吸,一步一步地解决这个问题”开头提示词显著提高了解决问题的效率。 这突出了精心选择的语言对生成式 AI 系统性能的影响。
掌握提示词最有效的用法,尤其是在 AI 技术快速发展的情况下,是一个持续的挑战。 您应该认识到提示词工程的重要性,并考虑利用社区和研究的见解来改进提示词创建策略。
创建有效提示词
在开发提示词时,整合几个关键组件以确保清晰度和有效性非常重要:
-
指令:向 AI 提供清晰直接的指令,就像您与人交流一样。这种清晰度对于帮助 AI“理解”预期内容至关重要。
-
外部上下文:在必要时包含相关的背景信息或 AI 响应的具体指导。这种“外部上下文”为提示词提供了框架,并帮助 AI 理解整体场景。
-
用户输入:这是直接的部分——用户的直接请求或问题构成了提示词的核心。
-
输出指示器:这方面可能很棘手。它涉及指定 AI 响应的所需格式,例如 JSON。但是,请注意 AI 可能并不总是严格遵守此格式。例如,它可能会在实际 JSON 数据之前加上“这是您的 JSON”之类的短语,或者有时会生成不准确的类似 JSON 的结构。
在编写提示词时,向 AI 提供预期问题和答案格式的示例非常有益。 这种做法有助于 AI“理解”您的查询结构和意图,从而产生更精确和相关的响应。 虽然本文档没有深入探讨这些技术,但它们为进一步探索 AI 提示词工程提供了一个起点。
以下是一些可供进一步研究的资源。
高级技术
-
零样本、少样本学习: 使模型能够在几乎没有特定问题类型先验示例的情况下做出准确的预测或响应,使用学习到的泛化来理解和执行新任务。
-
思维链: 链接多个 AI 响应以创建连贯且上下文感知的对话。它帮助 AI 保持讨论的线索,确保相关性和连续性。
-
ReAct (思考 + 行动): 在这种方法中,AI 首先分析(思考)输入,然后确定最合适的行动方案或响应。它将理解与决策相结合。
微软指南
-
提示词创建和优化框架: 微软提供了一种结构化的方法来开发和完善提示词。该框架指导用户创建有效的提示词,从 AI 模型中获得所需的响应,优化交互以实现清晰度和效率。
令牌
令牌在 AI 模型处理文本的方式中至关重要,它充当将我们理解的单词转换为 AI 模型可以处理的格式的桥梁。 这种转换分两个阶段发生:单词在输入时转换为令牌,这些令牌然后在输出时转换回单词。
分词是将文本分解为令牌的过程,是 AI 模型理解和处理语言的基础。 AI 模型使用这种分词格式来理解和响应提示词。
为了更好地理解令牌,可以将它们视为单词的一部分。通常,一个令牌代表大约四分之三的单词。例如,莎士比亚的全部作品,总计约 900,000 个单词,将转换为大约 120 万个令牌。
尝试使用 OpenAI Tokenizer UI 来查看单词是如何转换为令牌的。
令牌除了在 AI 处理中的技术作用外,还具有实际意义,尤其是在计费和模型功能方面:
-
计费:AI 模型服务通常根据令牌使用量计费。输入(提示词)和输出(响应)都计入总令牌数,因此较短的提示词更具成本效益。
-
模型限制:不同的 AI 模型具有不同的令牌限制,定义了它们的“上下文窗口”——它们一次可以处理的最大信息量。例如,GPT-3 的限制是 4K 令牌,而像 Claude 2 和 Meta Llama 2 这样的其他模型的限制是 100K 令牌,一些研究模型可以处理多达 100 万个令牌。
-
上下文窗口:模型的令牌限制决定了其上下文窗口。超出此限制的输入不会被模型处理。发送最少有效的信息集进行处理至关重要。例如,在询问“哈姆雷特”时,无需包含莎士比亚所有其他作品的令牌。
-
响应元数据:AI 模型响应的元数据包括使用的令牌数量,这是管理使用情况和成本的重要信息。