代理机制
Spring AOP 使用 JDK 动态代理或 CGLIB 为给定的目标对象创建代理。JDK 动态代理内置于 JDK 中,而 CGLIB 是一种常见的开源类定义库(重新打包到 spring-core 中)。
如果被代理的目标对象至少实现了一个接口,则使用 JDK 动态代理,并且代理目标类型实现的所有接口。
如果目标对象未实现任何接口,则会创建一个 CGLIB 代理,它是目标类型的运行时生成的子类。
如果您想强制使用 CGLIB 代理(例如,代理为目标对象定义的每个方法,而不仅仅是其接口实现的方法),
您可以这样做。但是,您应该考虑以下问题:
-
final类不能被代理,因为它们不能被扩展。 -
final方法不能被通知,因为它们不能被覆盖。 -
private方法不能被通知,因为它们不能被覆盖。 -
不可见的方法——例如,来自不同包的父类中的包私有方法——不能被通知,因为它们实际上是私有的。
-
您的代理对象的构造函数不会被调用两次,因为 CGLIB 代理实例是通过 Objenesis 创建的。但是,如果您的 JVM 不允许构造函数绕过,您可能会看到双重调用以及来自 Spring AOP 支持的相应调试日志条目。
-
您的 CGLIB 代理使用可能会面临 Java 模块系统的限制。通常情况下,当部署在模块路径上时,您无法为
java.lang包中的类创建 CGLIB 代理。此类情况需要 JVM 引导标志--add-opens=java.base/java.lang=ALL-UNNAMED,该标志不适用于模块。
强制使用特定的 AOP 代理类型
要强制使用 CGLIB 代理,请将 <aop:config> 元素的 proxy-target-class 属性值设置为 true,如下所示:
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<!-- other beans defined here... -->
</aop:config>当您使用 @AspectJ 自动代理支持时,要强制使用 CGLIB 代理,请将 <aop:aspectj-autoproxy> 元素的 proxy-target-class 属性设置为 true,如下所示:
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"/>|
多个 |
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy、@EnableTransactionManagement 和相关的配置注解提供了相应的 proxyTargetClass 属性。这些也会合并成一个统一的自动代理创建器,从而在运行时有效地应用_最强_的代理设置。从 7.0 开始,这也适用于单个代理处理器,例如 @EnableAsync,它们始终参与给定应用程序中所有自动代理尝试的统一全局默认设置。
全局默认代理类型在不同设置之间可能有所不同。虽然核心框架默认建议基于接口的代理,但 Spring Boot 可能会根据配置属性默认启用基于类的代理。
从 7.0 开始,可以通过在给定 @Bean 方法或 @Component 类上使用 @Proxyable 注解来强制为单个 bean 使用特定的代理类型,其中 @Proxyable(INTERFACES) 或 @Proxyable(TARGET_CLASS) 会覆盖任何全局配置的默认值。对于非常特殊的用途,您甚至可以通过 @Proxyable(interfaces=…) 指定要使用的代理接口,从而将暴露限制为选定的接口,而不是目标 bean 实现的所有接口。
理解 AOP 代理
Spring AOP 是基于代理的。在您编写自己的切面或使用 Spring Framework 提供的任何基于 Spring AOP 的切面之前,理解最后这句话的实际含义至关重要。
首先考虑一个您有一个普通的、未代理的对象引用的场景,如下面的代码片段所示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
public class SimplePojo implements Pojo {
public void foo() {
// this next method invocation is a direct call on the 'this' reference
this.bar();
}
public void bar() {
// some logic...
}
}class SimplePojo : Pojo {
fun foo() {
// this next method invocation is a direct call on the 'this' reference
this.bar()
}
fun bar() {
// some logic...
}
}如果您在一个对象引用上调用一个方法,该方法将直接在该对象引用上被调用,如下面的图片和列表所示:
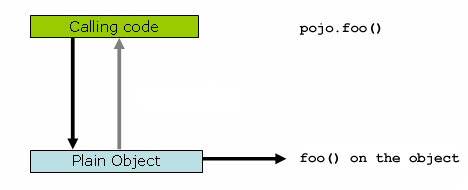
-
Java
-
Kotlin
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Pojo pojo = new SimplePojo();
// this is a direct method call on the 'pojo' reference
pojo.foo();
}
}fun main() {
val pojo = SimplePojo()
// this is a direct method call on the 'pojo' reference
pojo.foo()
}当客户端代码持有的引用是一个代理时,情况会略有不同。请看下面的图表和代码片段:
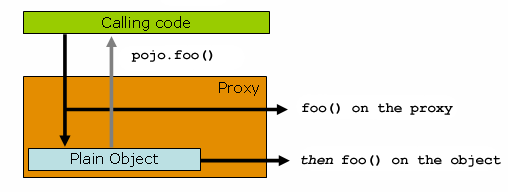
-
Java
-
Kotlin
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProxyFactory factory = new ProxyFactory(new SimplePojo());
factory.addInterface(Pojo.class);
factory.addAdvice(new RetryAdvice());
Pojo pojo = (Pojo) factory.getProxy();
// this is a method call on the proxy!
pojo.foo();
}
}fun main() {
val factory = ProxyFactory(SimplePojo())
factory.addInterface(Pojo::class.java)
factory.addAdvice(RetryAdvice())
val pojo = factory.proxy as Pojo
// this is a method call on the proxy!
pojo.foo()
}这里要理解的关键是 Main 类的 main(..) 方法中的客户端代码持有一个对代理的引用。这意味着对该对象引用的方法调用是对代理的调用。因此,代理可以将调用委托给与该特定方法调用相关的所有拦截器(通知)。但是,一旦调用最终到达目标对象(在本例中是 SimplePojo 引用),它可能对自己进行的任何方法调用,例如 this.bar() 或 this.foo(),都将针对 this 引用而不是代理进行调用。这具有重要的影响。这意味着自调用不会导致与方法调用相关的通知有机会运行。换句话说,通过显式或隐式 this 引用进行的自调用将绕过通知。
为了解决这个问题,您有以下选择。
- 避免自调用
-
最好的方法(这里的“最好”一词是宽泛地使用)是重构您的代码,使自调用不会发生。这确实需要您付出一些努力,但它是最好、侵入性最小的方法。
- 注入自引用
-
另一种方法是利用 自注入,并通过自引用而不是通过
this调用代理上的方法。 - 使用
AopContext.currentProxy() -
最后这种方法强烈不建议使用,我们不情愿地指出它,更倾向于前面的选项。但是,作为最后的手段,您可以选择将类中的逻辑绑定到 Spring AOP,如下面的示例所示。
-
Java
-
Kotlin
public class SimplePojo implements Pojo {
public void foo() {
// This works, but it should be avoided if possible.
((Pojo) AopContext.currentProxy()).bar();
}
public void bar() {
// some logic...
}
}class SimplePojo : Pojo {
fun foo() {
// This works, but it should be avoided if possible.
(AopContext.currentProxy() as Pojo).bar()
}
fun bar() {
// some logic...
}
}使用 AopContext.currentProxy() 会使您的代码完全耦合到 Spring AOP,并且使类本身意识到它正在 AOP 上下文中使用,这会降低 AOP 的一些好处。它还需要将 ProxyFactory 配置为暴露代理,如下面的示例所示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProxyFactory factory = new ProxyFactory(new SimplePojo());
factory.addInterface(Pojo.class);
factory.addAdvice(new RetryAdvice());
factory.setExposeProxy(true);
Pojo pojo = (Pojo) factory.getProxy();
// this is a method call on the proxy!
pojo.foo();
}
}fun main() {
val factory = ProxyFactory(SimplePojo())
factory.addInterface(Pojo::class.java)
factory.addAdvice(RetryAdvice())
factory.isExposeProxy = true
val pojo = factory.proxy as Pojo
// this is a method call on the proxy!
pojo.foo()
}|
AspectJ 编译时织入和加载时织入没有这个自调用问题,因为它们在字节码内部而不是通过代理应用通知。 |