Spring Batch Architecture
Spring Batch 的设计考虑到了可扩展性和各种最终用户。以下图片展示了支持终端用户开发人员的可扩展性和易用性的分层架构。
.Spring Batch Layered Architecture
image::spring-batch-layers.png[]
此分层架构突出了三个主要的顶级组件:应用程序、核心和基础设施。应用程序包含所有批次作业和使用 Spring Batch 编写的开发人员的自定义代码。批次核心包含启动和控制批次作业所需的运行时核心类。它包括 JobLauncher、Job 和 Step 的实现。应用程序和核心都建立在通用的基础架构之上。此基础架构包含通用的读取器、编写器和服务(如 RetryTemplate),这些内容由应用程序开发人员(读取器和编写器,如 ItemReader 和 ItemWriter)和核心框架本身(retry,这是其自己的库)使用。
General Batch Principles and Guidelines
在构建批处理解决方案时,应考虑以下主要原则、准则和一般注意事项。
-
记住,批处理架构通常会影响在线架构,反之亦然。尽可能是,通过使用通用构建模块,来兼顾两种架构和环境进行设计。
-
尽可能简化,避免在单个批处理应用程序中构建复杂的逻辑结构。
-
保持数据处理和存储在物理上尽可能靠近(换句话说,让你的数据保存在处理发生的位置)。
-
将系统资源使用最小化,尤其是 I/O。尽可能在内部内存中执行尽可能多的操作。
-
查看应用程序 I/O(分析 SQL 语句),以确保避免了不必要的物理 I/O。具体来说,需要留意以下四个常见缺陷:
-
为每笔交易读取数据,而这些数据可以一次读取并进行缓存或保存在工作存储中。
-
重新读取一笔交易的数据,而这些数据已经在同一交易的前面读取过。
-
导致不必要对表或索引进行扫描。
-
未在 SQL 语句的
WHERE子句中指定键值。
-
-
在批处理运行中不要做两遍事情。举例来说,如果你需要数据汇总以报告目的,你应该(如果可能的话)在数据被最初处理时增加存储的总数,这样你的报告应用程序就不必重新处理相同的数据了。
-
在批处理应用程序的开始分配足够的内存以避免在进程期间耗时的重新分配。
-
始终假设是最差的数据完整性。插入足够的检查和记录验证以维护数据完整性。
-
在可能的情况下实现内部验证的校验和。例如,平面文件应该有一个尾部记录来告知文件中的记录总数和键字段的总和。
-
在容量实际的环境中尽早规划并执行压力测试,并使用现实的数据量。
-
在大型批处理系统中,备份可能具有挑战性,尤其是如果系统在 24/7 全天运行且与在线应用程序并发运行的话。数据库备份通常在在线设计中得到很好的解决,但文件备份应该被认为是同样重要的。如果系统依赖平面文件,则文件备份过程不仅应该到位并记录下来,还应该定期测试。
Batch Processing Strategies
为了帮助设计和实施批处理系统,应以示例结构图和代码壳的形式,向设计师和程序员提供基本的批处理应用程序构建模块和模式。开始设计批处理作业时,应将业务逻辑分解为一系列可通过以下标准构建模块实施的步骤:
-
Conversion Applications: 对于外部系统提供或生成的每种类型文件,必须创建一个转换应用程序来将提供的交易记录转换成处理所需的标准格式。这种类型的批处理应用程序可以部分或完全由翻译实用工具模块(见基本批处理服务)组成。
-
Validation Applications: 验证应用程序确保所有输入和输出记录都是正确且一致的。验证通常基于文件头和文件尾、校验和和验证算法以及记录级别交叉检查。
-
Extract Applications: 抽取应用程序从数据库或输入文件读取一组记录,根据预定义规则选择记录,并将记录写入一个输出文件。
-
Extract/Update Applications: 抽取/更新应用程序从数据库或输入文件读取记录,并通过每个输入记录中找到的数据对数据库或输出文件进行更改。
-
Processing and Updating Applications: 处理和更新应用程序对来自抽取或验证应用程序的输入交易执行处理。处理通常涉及读取数据库以获取处理所需的数据,可能更新数据库并创建用于输出处理的记录。
-
Output/Format Applications: 输出/格式应用程序读取输入文件,根据记录中的排序密钥字段按照标准格式重新组织数据,并为打印或传输到其他程序或系统生成输出文件。
此外,还应为无法使用前面提到的构建模块构建的业务逻辑提供基本的应用程序外壳。
除了主要构建模块外,每个应用程序还可能使用一个或多个标准实用步骤,例如:
-
排序:一个程序,它读取输入文件并生成输出文件,在其中记录已按照记录中的排序键字段重新排序。排序通常由标准系统实用工具执行。
-
拆分:一个程序,它读取单个输入文件并将每个记录写入多个输出文件中,根据字段值。拆分可以依据参数驱动的标准系统实用工具量身定制或执行。
-
合并:一个程序,它从多个输入文件读取记录,并生成一个包含来自输入文件的合并数据的输出文件。合并可以依据参数驱动的标准系统实用工具量身定制或执行。
批处理应用程序还可以按其输入源进行分类:
-
数据库驱动的应用程序由从数据库检索的行或值驱动。
-
文件驱动的应用程序由从文件检索的记录或值驱动。
-
消息驱动的应用程序由从消息队列检索的消息驱动。
任何批处理系统的基础都是处理策略。影响策略选择因素包括:预计的批处理系统量、与联机系统或其他批处理系统的并发性以及可用的批处理窗口。(请注意,随着越来越多的企业希望全天候运转,清晰的批处理窗口正在消失)。
批处理的典型处理选项(按实施复杂性的递增顺序):
-
在脱机模式下批处理窗口期间的正常处理。
-
并发批处理或在线处理。
-
同时对多个不同的批处理运行或作业进行并行处理。
-
分区(同时处理同一作业的多个实例)。
-
上述选项的组合。
商业调度程序可能支持其中某些或所有选项。
本节的其余部分将更详细地讨论这些处理选项。请注意,通常情况下,批处理所采用的提交和锁定策略取决于执行的处理类型,且联机锁定策略也应使用相同的原则。因此,在设计整体架构时,批处理架构不能仅仅是事后考虑。
锁定策略可以是仅使用普通数据库锁或在架构中实现其他自定义锁定服务。该锁定服务将跟踪数据库锁定(例如,通过将必要信息存储在专用数据库表中),并向请求数据库操作的应用程序程序授予或拒绝权限。此架构还可以实现重试逻辑,以避免在锁定情况下中止批处理作业。
*1. 在批处理窗口中的正常处理*对于在单独的批处理窗口中运行的简单批处理进程(其中更新的数据不受联机用户或其他批处理进程需要),并发性不是问题,且可以在批处理运行结束时执行一次提交。
在大多数情况下,更有效果的办法更为合适。请记住,随着时间的推移,批处理系统在复杂性和处理的数据量这两方面都有增长的趋势。如果未采用锁定策略,且系统仍依赖于单一提交点,则修改批处理程序可能很痛苦。因此,即使对于最简单的批处理系统,也要考虑重启恢复选项所需的提交逻辑,以及本节稍后描述的更复杂情况相关信息。
*2. 并发批处理或联机处理*处理数据(可由联机用户同时更新)的批处理应用程序不得锁定联机用户可能需要且超过几秒的数据(无论在数据库中还是在文件中)。此外,应在每几个事务结束时将更新提交到数据库。这样做可最大程度减少对其他流程不可用的数据量以及数据不可用的经过时间。
最大程度减少物理锁定的另一个选项是实现逻辑行级锁定,可使用乐观锁定模式或悲观锁定模式。
-
乐观锁定假设记录争用的可能性低。它通常是指在每个同时由批处理和在线处理使用的数据库表中插入一个时间戳列。当应用程序获取一行来处理时,它还获取时间戳。随后,当应用程序尝试更新已处理的行时,更新将在
WHERE子句中使用原始时间戳。如果时间戳匹配,则更新数据和时间戳。如果时间戳不匹配,则表示另一个应用程序已在获取和更新尝试之间更新了同一行。因此,不能执行更新。 -
悲观锁定是指任何假设记录争用可能性高的锁定策略,因此在检索时需要获取物理锁或逻辑锁。一种悲观逻辑锁使用数据库表中专用的锁列。当应用程序检索要更新的行时,它将在锁列中设置一个标志。如果标志设置完成,则试图检索同一行的其他应用程序在逻辑上将失败。当设置标志的应用程序更新行时,它还将清除标志,以便其他应用程序能够检索该行。请注意,在初始获取和设置标志之间也必须维护数据完整性——例如,通过使用数据库锁(例如
SELECT FOR UPDATE)。另外请注意,此方法与物理锁有相同的缺点,只是在构建超时机制方面稍容易一些,该机制可在用户离开时释放锁,而记录仍被锁定。
这些模式不一定要适用于批处理,但它们可能用于并发批处理和联机处理(例如在数据库不支持行级锁定的情况下)。通常情况下,乐观锁定更适用于联机应用程序,而悲观锁定更适用于批处理应用程序。每当使用逻辑锁定时,都必须对所有访问受逻辑锁定保护的数据实体的应用程序使用相同的方案。
请注意,这两种解决方案都只解决了对单个记录的锁定。通常,我们可能需要锁定一个合乎逻辑的记录组。对于物理锁,您必须非常小心地管理这些锁,以避免潜在的死锁。对于逻辑锁,最好构建一个了解您要保护的逻辑记录组并能确保锁定连贯且无死锁的逻辑锁定管理器。该逻辑锁定管理器通常使用自己的表进行锁定管理、争用报告、超时机制和其他事项。
*3. 并行处理*并行处理可让多个批处理运行或作业并行运行,以最大程度减少总的经过批处理时间。只要作业不共享相同的文件、数据库表或索引空间,这不是问题。如果他们这样做,应使用分区数据来实现此服务。另一个选项是构建一个架构模块,通过使用控制表来维护相互依存关系。控制表应为每个共享资源包含一行,并且无论它是否被应用程序使用。然后,批处理架构或并行作业中的应用程序将从该表中检索信息,以确定它能否访问它所需的资源。
如果数据访问不是问题,则可通过使用其他线程并行处理来实现并行处理。在大型机环境中,传统上使用并行作业类,以确保所有流程具有足够的 CPU 时间。无论如何,该解决方案必须足够健壮,以确保为所有正在运行的流程提供时间片。
并行处理中的其他关键问题包括负载平衡和常规系统资源(例如文件、数据库缓冲池等)的可用性。此外,请注意,控制表本身很容易成为一个关键资源。
*4. 分区*使用分区可以让大型批处理应用程序的多个版本同时运行。这样做的目的是减少处理较长的批处理作业所需的经过时间。可以成功分区的是输入文件可以拆分或主数据库表分区的进程,以使应用程序可以针对不同的数据集运行。
此外,分区处理必须仅处理其分配的数据集。分区架构必须与数据库设计和数据库分区策略紧密关联。请注意,数据库分区不一定指数据库的物理分区(尽管在大多数情况下,物理分区是适宜的)。下图说明了分区方法:
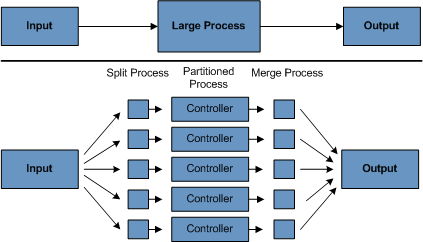
该架构应足够灵活,以允许动态配置分区数。您应同时考虑自动和用户控制配置。自动配置可基于输入文件大小和输入记录数等参数。
4.1 分区方法 根据具体情况选择分区方法。以下列表描述了一些可能的分区方法:
1. 固定且均匀的数据集拆分
这涉及将输入记录集拆分为均等数量的部分(例如 10 个,其中每个部分刚好有整个记录集的 1/10)。然后,批处理/提取应用程序的一个实例处理每个部分。
要使用此方法,需要进行预处理以拆分记录集。此拆分的最终结果是可以用作批处理/提取应用程序输入的较低和较高边界范围号,以便将其处理限制为其相应部分。
预处理可能是一项巨大的开销,因为它必须计算和确定记录集每个部分的边界。
2. 根据一个键列进行拆分
这涉及根据键列(例如位置代码)拆分输入记录集,并将每个键的数据分配给一个批处理实例。要实现此目的,列值可以为:
-
通过分区表(在本文档后面的部分中描述)分配到批处理实例。
-
通过部分值分配到批处理实例(例如 0000-0999、1000 - 1999,依此类推)。
在选项 1 中,添加新值意味着手动重新配置批处理或提取,以确保将新值添加到特定实例中。
在选项 2 中,这可确保所有值均被批处理作业的一个实例覆盖。但是,一个实例处理的值的数量取决于列值的分布(在 0000-0999 范围内可能有很多位置,而在 1000-1999 范围内则很少)。在此选项下,数据范围应在考虑分区的情况下进行设计。
在两种选项下,都无法实现记录向批处理实例的优化均匀分布。所使用的批处理实例数量没有动态配置。
3. 根据视图进行拆分
此方法基本上是根据键列进行拆分,但在数据库级别上进行。它涉及将记录集拆分为视图。批处理应用程序的每个实例都在处理过程中使用这些视图。此拆分通过对数据进行分组来完成。
使用此选项时,必须将批处理应用程序的每个实例配置为连接到特定视图(而不是主表)。而且,随着新数据值的添加,必须将此新数据组包括到视图中。由于实例数量的变化会导致视图的变化,因此没有动态配置功能。
4. 添加处理指示符
这涉及为输入表添加一个新列,此新列充当指示符。作为预处理步骤,所有指示符均标记为未处理。在批处理应用程序的记录提取阶段,在个别记录被标记为未处理,且记录一经读取(带锁)即被标记为正在处理的条件下,读取记录。该记录完成后,指示符更新为已完成或出错。您无需更改即可启动批处理应用程序的多个实例,因为附加的列可确保记录仅处理一次。
使用此选项会动态增加表上的 I/O。在更新批处理应用程序的情况下,此影响会减小,因为无论如何都必须进行写入。
5. 将表提取到平面文件中
此方法涉及将表提取到平面文件中。然后可以将此文件拆分为多个段并用作批处理实例的输入。
对于这种方案,将表提取到一个文件中并对其进行拆分的额外开销可能会抵消多分区的影响。可通过更改文件拆分脚本来实现动态配置。
6. 使用哈希列
此方案涉及向用来检索驱动程序记录的数据库表添加一个哈希列(键或索引)。此哈希列带有指示符,以确定批处理应用程序的哪个实例处理此特定行。例如,如果要启动三个批处理实例,指示符“A”标记要由实例 1 处理的行,指示符“B”标记要由实例 2 处理的行,指示符“C”标记要由实例 3 处理的行。
然后,用于检索记录的过程将附加一个 WHERE 从句,以选择由特定指示符标记的所有行。此表中的插入涉及添加标记字段,该标记字段将默认为一个实例(例如“A”)。
将使用一个简单的批处理应用程序来更新指示符,例如在不同的实例之间重新分配负载。当添加了足够多的新行时,可以随时(批处理窗口除外)运行此批处理以将新行重新分配到其他实例。
批处理应用程序的其他实例只需要运行批处理应用程序(如前面的段落中所述)即可将指示符重新分配为与新的实例数一起工作。
4.2 数据库和应用程序设计原则
支持针对分区数据库表运行并使用键列方法的多分区应用程序的架构应该包含一个中央分区存储库,用于存储分区参数。这提供了灵活性并确保可维护性。该存储库通常由一个称为分区表的表组成。
存储在分区表中的信息是静态的,通常应由数据库管理员维护。该表应包含多分区应用程序每个分区的行信息。该表应具有列,用于程序 ID 代码、分区号(分区的逻辑 ID)、此分区的数据库键列的低值以及此分区的数据库键列的高值。
在程序启动时,程序 id 和分区号应从架构(特别是从控制处理小任务)传递到应用程序。如果使用了键列方法,这些变量将用于读取分区表以确定应用程序要处理的数据范围。此外,必须在整个处理过程中使用分区号才能:
-
添加到输出文件或数据库更新,以便合并流程正常工作。
-
向批处理日志报告正常处理,向架构错误处理程序报告任何错误。
4.3 最小化死锁
当应用程序并行运行或被分区时,可能会争用数据库资源并发生死锁。作为数据库设计的一部分,至关重要的是,数据库设计团队尽可能消除潜在的争用情况。
此外,开发人员必须确保数据库索引表的在设计时考虑了死锁预防和性能。
死锁或热点通常发生在管理或架构表中,例如日志表、控制表和锁表。应该考虑这些影响。现实的压力测试对于识别架构中可能的瓶颈至关重要。
为了最大程度地降低冲突对数据的影响,该架构应该在连接到数据库或遇到死锁时提供服务(例如等待和重试间隔)。这意味着一种内置机制,用于对某些数据库返回代码做出反应,并且在发出立即错误之前,等待预定的时间并重试数据库操作。
4.4 参数传递和验证
分区架构对于应用程序开发人员而言应该是相对透明的。该架构应该执行与在分区模式下运行应用程序相关的所有任务,包括:
-
在应用程序启动之前检索分区参数。
-
在应用程序启动之前验证分区参数。
-
在启动时将参数传递给应用程序。
验证应包括检查以确保:
-
应用程序有足够的分区来覆盖整个数据范围。
-
分区之间没有间隙。
如果数据库被分区,可能需要进行一些额外的验证,以确保单个分区不会跨越数据库分区。
此外,架构应考虑合并分区。关键问题包括:
-
在进入下一步作业之前是否必须完成所有分区?
-
如果其中的一个分区中止,会发生什么?